2025-01-06
indicators
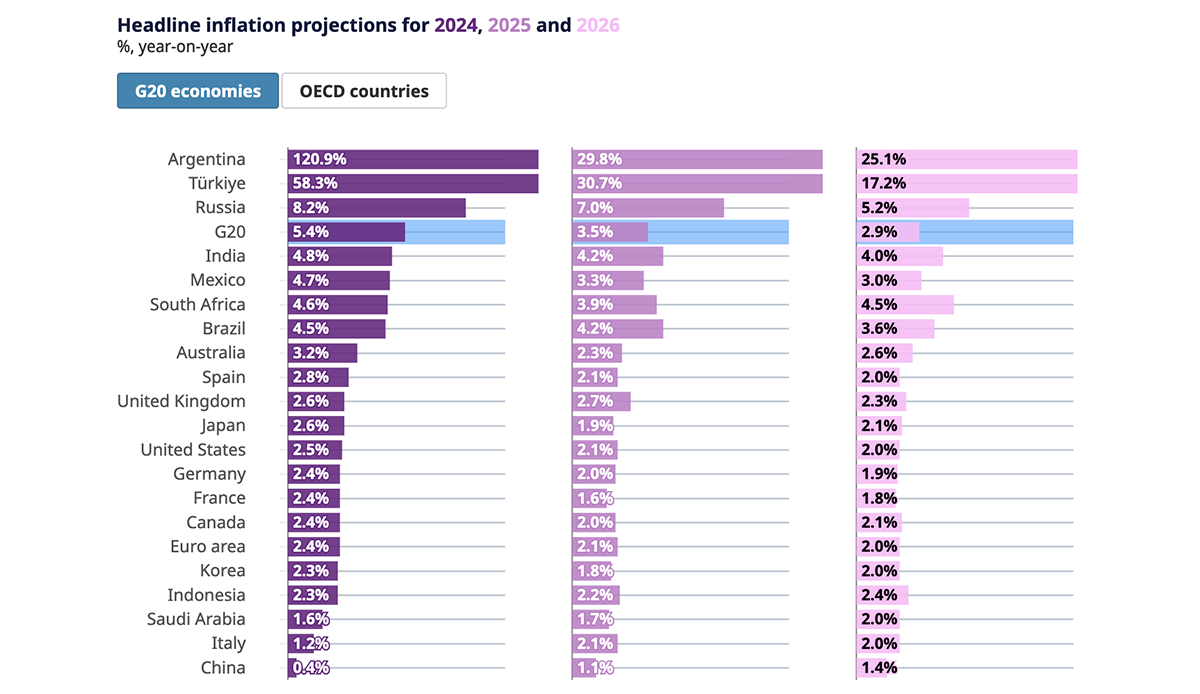
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has released its Economic Outlook for December 2024, presenting a cautiously optimistic view of the global economy. The report forecasts a modest increase in global GDP growth, projecting a rise from 3.2% in 2024 to 3.3% in both 2025 and 2026. This anticipated growth is attributed to declining inflation rates, which are expected to bolster real incomes and consumer spending.  In OECD member countries, GDP growth is projected to stabilize at 1.9% for both 2025 and 2026, reflecting a steady economic environment. Non-OECD economies, particularly in emerging Asian markets, are expected to maintain their current growth trajectories, continuing to be significant contributors to global economic expansion. The report highlights a continued decline in headline inflation across most nations throughout 2024, driven by reductions in food, energy, and goods prices. This downward trend in inflation is anticipated to persist, further supporting real income growth and enhancing consumer purchasing power. Despite these positive indicators, the OECD cautions that the economic outlook remains highly uncertain. Potential risks include escalating geopolitical tensions and the implementation of global trade restrictions, which could impede further disinflation and dampen economic growth prospects. Additionally, unforeseen shocks may lead to disruptive corrections in financial markets, exacerbated by high debt levels and stretched asset valuations. To mitigate these risks and strengthen economic foundations, the OECD emphasizes the need for ambitious structural policy reforms. Key recommendations include enhancing education and skills development, reducing labor and product market constraints to encourage investment and labor mobility, and increasing public investment in areas with significant market failures. Such measures are deemed essential to improve productivity, facilitate the adoption of new technologies, and boost labor force participation, thereby promoting sustainable and inclusive growth in the medium term. In summary, while the OECD’s latest Economic Outlook presents a slightly more optimistic forecast for the global economy, it underscores the fragility of this recovery and the critical importance of policy interventions to sustain and enhance economic growth. Note: Table shows harmonised index of consumer prices for the euro area and its member states and the United Kingdom, and national consumer price index for all other countries. Source: OECD Economic Outlook, December 2024

